Music Theory 1: Intervals & Scales
October 3, 2021
DARK DAIRY
October 8, 2021Introduction to Gym Equipment.
Have you ever walked into a gym and felt intimidated by the various types of workout equipment spaced out over the entire floor? Not to mention the rows of machines in the cardio section of the gym.
Actually, everyone has. So you are not alone.
This blog is aimed at informing new gym-goers about the types of machines one would encounter in todays modern gyms. What each one is designed for and how to use them effectively to extract the maximum benefit.
Also Read: Warmup before Lifting
Categories of gym equipment
In the basic gym you will find two categories of equipment:
Weight Training and Cardiovascular
We will be considering the equipment available in these two niches of the standard gym and not the equipment used in alternate trends, for example, cross-training equipment.
The brand and type of equipment available will never be exactly the same and will vary from gym to gym.
The most common standard is Nautilus machines.
You should always also read the specific instructions on the equipment found in your gym, which will most likely be pasted somewhere visible on the machine.
There are basic movements that work specific muscle groups. You cant exercise the biceps by bending your knees, you would have to bend your elbow.
This leads to machines working the same muscle group to look similar although the manufacturers vary.
A chest press machine, no matter who the manufacturer is, will look like a chest press machine.
Machines are built either for:
Compound Movements: Movements involving multiple muscle groups.
Or,
Isolation Movements: Movements targeting a specific muscle.
Types of Equipment:
Weight Training
CHEST PRESS MACHINE

Exercise – Compound
Primary Muscle – Chest
Muscles under Tension – Chest, Shoulders, Triceps
Ergonomics: The grips need to be at the nipple line, adjust the seat height to achieve this.
Adjust the seat forward or backward so that the maximum range of motion is achieved without the weight stack getting locked at the top or resting on the stationary weights at the bottom in the starting position.
Execution: Exhale while you slowly press the handles out. Arms should be extended almost straight but not locked out. Inhale while slowly returning the handles to the start position.
Repeat for the desired number of reps.
PEC FLY MACHINE

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle – Chest or Rear Deltoid
Muscles under Tension – Chest or Shoulders
Ergonomics: With the pin above the head adjust the handles at a distance apart that gives a good stretch across the chest. Ensure the weight stack does not rest on the stationary weights between reps. Keep your back straight and feet flat on the floor or foot-stand. Place your head and neck firmly against the back-pad. Adjust the seat height so that the handles are at chest level.
This machine is also used for Rear Deltoid Isolation movements. In order to work this muscle group you would sit facing the weight stack and hold the handles which are parallel to the floor. Seat height would be adjusted so that your arms are parallel to the floor or just a bit lower is also fine to isolate the rear shoulder. The movement would be opposite to that of the chest fly.
Execution: Exhale as you slowly bring the pads together till they meet in front of your chest.
For rear deltoids: exhale as you pull your arms back till they are at right angles with your body.
Repeat for the desired amount of reps.
SHOULDER PRESS MACHINE

Exercise – Compound
Primary Muscle – Front and Side Deltoids
Muscles under Tension – Shoulders, Triceps
Ergonomics: Adjust the seat so that the grip handles are between the shoulder and ear
level. Maintain a straight back and firm midsection.
Execution: Push the handles overhead with your elbows slightly bent and upper arms
vertical, and in a controlled motion, lower the handles back to the starting position. Keep the muscles under tension between reps by not lowering the handles to the point when the weights rest on the rack. Repeat for the desired amount of reps.
SIDE LATERAL RAISE MACHINE

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle – Side Deltoids
Muscles under Tension – Side Deltoids, Trapezius
Ergonomics: Adjust the seat height so that the pads are above your elbows and not more than halfway to your shoulders. Retract your shoulder blades and hold the grips while keeping elbows bent at 90
degrees.
Execution: Raise arms out sideways till your upper arms are parallel to the floor. Return in a controlled manner to the start position.
Caution: Do not use very heavy weights on this machine as the side deltoid is a relatively small muscle and you could injure the shoulder socket as well. Keep repetitions in the higher than usual range and an average of 15 would ensure that the weight used is not beyond your capacity.
FRONT LAT PULLDOWN

Exercise – Compound
Primary Muscle – Lats, Upper/mid Back
Muscles under Tension: Lats, Biceps, Middle Back
Ergonomics: Hold the bar just past the bend on each side, if your body width doesn’t allow this use a narrower bar, keeping your thumbs over the bar. Stretch your upper body and keep the natural arch in the lower back throughout the movement.
Execution: Lean back slightly and pull the bar down till it reaches chin level. Slowly return to the start position while straightening your body completely aiming for a full stretch in the latissimus dorsi (upper back). Repeat for the desired number of reps.
CABLE ROW MACHINE

Exercise – Compound
Primary Muscle – Upper and Mid Back
Muscles under Tension: Lats, Biceps, Middle Back, Lower Back
Ergonomics: Body position is key here. Keep the body and core tight and back straight while you hold the handles. Keep your feet firmly on the foot stand. Do not lock your knees.
Execution: Retract your shoulder blades and slowly pull the handles toward you, keeping your forearms at right angles and parallel to the floor. Bring your elbows as far back as possible. Controlled return to the starting position. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
BICEPS CURL MACHINE

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle: Biceps
Muscles under Tension: Biceps
Ergonomics: Seat height should allow for natural shoulder position, not higher or lower than normal. The arms should match the slant of the pad comfortably.
Execution: Exhale as you slowly raise the bar towards your chin, return slowly to the start position.
Caution: Keep arms in contact with the pad throughout the exercise to avoid pressure on the shoulder and elbow.
TRICEPS EXTENSION MACHINE
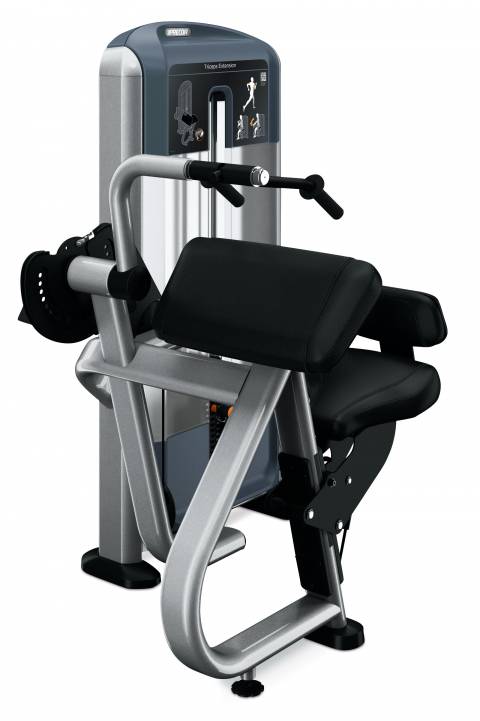

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle: Triceps
Muscle under Tension – Triceps
Ergonomics: Maintain good posture and keep your core tight. Very similar to the bicep curling machine except that when you hold the handles your entire arm is not resting o the padding but only the back of your upper arm is.
Execution: Push the handles down until your arm is fully extended and slowly return to the start position. Repeat for reps.
SMITH MACHINE

Exercise – Compound
Primary Muscle – Quads, Lower Back, Shoulders
Muscle under Tension – Depending on exercise almost Whole Body
Note: This piece of equipment can be used for Squats, Deadlifts, and Shoulder Presses.
It is used as a safety measure as the bar rides on guides and safety stoppers are available in case of an emergency.
For example, if you are squatting and can’t finish the last rep rising back up, just engage the safety mechanism and walk out from under the bar, unlike a free bar where you would go down under the weight. It enhances safety and allows you to push for that elusive last rep. However, strict form is always important to prevent injury.
LEG PRESS MACHINE

Exercise – Compound
Primary Muscle – Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Calves
Muscles under Tension – Entire lower body and Core
Ergonomics: Adjust the backrest and the foot base relative to each other to attain a 90-degree angle with the knees without the weight stack bottoming out.
Execution: Inhale while lowering the weight. Do not go below a 90-degree knee angle if you have a knee problem or want to prevent long-term injury.
Exhale while straightening legs underweight. Keep the core tight or use a weight belt.
Caution: Do not lock the knees when extending but keep a slight bend.
LEG EXTENSION MACHINE

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle – Quadriceps
Muscle under Tension – Quadriceps
Ergonomics: Set the lower leg pad at just above the top of the shoe, above the lower ankle. Your knees should have a 90-degree angle.
Execution: Exhale as you slowly straighten your legs to a soft lock position. Inhale and return to the start position.
Perform the desired amount of reps.
SEATED LEG CURL MACHINE

Exercise- Isolation
Primary Muscle – Hamstring
Muscle under Tension – Hamstring
Ergonomics: Lie down and let the pads contact the rear of your leg just above the Achilles tendon. Do not rest it high on the calves.
Execution: Exhale as you slowly lift the pads by bending the knees and mimic trying to touch your butt with the back of your shoe. Slowly return to the start for the required reps.
ADDUCTOR OR INNER THIGH MACHINE

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle – Inner Thigh
Muscle under Tension – Inner Thigh
Ergonomics: keep the seat as upright as possible while allowing for comfortable movement. Keep the pads at a comfortable distance apart.
Caution: Be careful not to stretch too far as contracting from an extended stretch would cause injury.
Execution: Squeeze the pads together, pausing when they touch, and return to start.
Repeat for required reps.
ABDOMINAL CRUNCH MACHINE

Exercise – Isolation
Primary Muscle – Abdominal Muscles
Muscles under Tension – Abdominal Muscles, Obliques
Ergonomics: Set the seat height as per preference with the waist at axis level. Grip the
handles and place elbows against the pads. Keep your head and neck neutral throughout and do not keep tense while performing the movement.
Execution: Exhale as you crunch forward only using the
abdominal muscles to do the work. Return to start position.
Tip: Do as many reps as possible and always to failure on each set performed. The abdominals are a workhorse of a muscle group so work them hard.
Cardiovascular
Stationary bike:

Adjust the seat of the bike so that your feet are firmly on the pedals. Keep your back straight and core firm. Cycle as you would do normally. Start slow and gently increase speed to a level at the edge of your comfort zone and maintain the calorie burn.
Elliptical or Cross Trainer:

An effective cardio machine that provides a considerate amount of calorie burn. Hold the handlebars and place your feet on each of the pedals. Keep your back straight, and start a combination of a cycling and jogging movement. This equipment is good for those who do not wish to overwork the knees as one would do while running.
STAIR CLIMBER:

This machine works on your lower body. Walk or climb just the way you do while climbing stairs. Good leg burn.
TREADMILL:

Running or walking on a treadmill, increasing the speed gradually until a brisk maintainable pace is reached, will burn a lot of calories quickly. You can also adjust the incline according to your preference to increase the burn.
With that, we cover the most common equipment you would encounter in the gym. So you would have a fair idea as to what you are looking at while scouting for a suitable gym.
You would also have a fair idea as to which gym would suit you best depending on your gym goals and exercise routine.
Remember: There is no need to fear the metal.
Additional Info: Home Workout